When buyers compare square tubing vs round tubing, the real decision is rarely about shape alone.
It is about strength under real loads, manufacturing consistency, surface finish, and total landed cost.
For OEM brands, retail buyers, and sourcing teams, choosing the wrong shape often shows up later—as higher reject rates, uncomfortable products, or unexpected cost increases.
This guide explains the practical differences that matter once a design moves from drawing to mass production.
Square Tubing vs Round Tubing: Quick Decision Summary
If you only remember one thing, remember this:
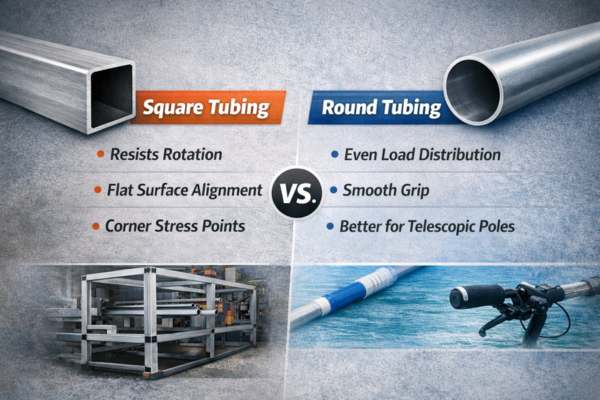
- Round tubing performs better under mixed-direction loads and is easier to manufacture consistently.
- Square tubing helps prevent rotation and aligns easily in fixed assemblies.
- In long, lightweight products, round tubing often delivers better strength-to-weight efficiency.
This is why many consumer and retail-facing products default to round tubing unless rotation control is critical.
Strength Comparison: Why Shape Changes Load Behavior

A common assumption is that square tubing is stronger. That is not always true.
Round tubing
- Distributes stress evenly around the circumference
- Handles bending from multiple directions more predictably
- Performs well in long-span or handheld applications
Square tubing
- Resists rotation when a load is applied on flat faces
- Can feel stiffer in one direction
- Concentrates stress at corners if the walls are thin
Key takeaway:
In products longer than 1.5–2 meters, round tubing usually shows more stable performance under real-world use.
Weight and Wall Thickness: Where Cost Starts to Shift

At the same outer dimension, shape affects how material is used.
- Round tubing typically achieves the required stiffness with thinner walls
- Square tubing often needs extra thickness to compensate for corner stress
- Thicker walls increase:
- Aluminum usage
- Extrusion pressure
- Finished product weight
For handheld or telescopic products, extra weight quickly turns into customer complaints.
Manufacturing Reality: Extrusion Consistency and Yield

On the factory floor, shape has a direct impact on yield and lead time.
Round tubing
- Easier die control during extrusion
- Better straightness over long lengths
- Higher first-pass yield in mass production
Square tubing
- More sensitive to die wear
- Higher risk of corner distortion
- Requires tighter process control to keep the wall thickness uniform
In high-volume orders, even a small yield difference can affect delivery schedules and unit cost.
Surface Finish and Cosmetic Risk
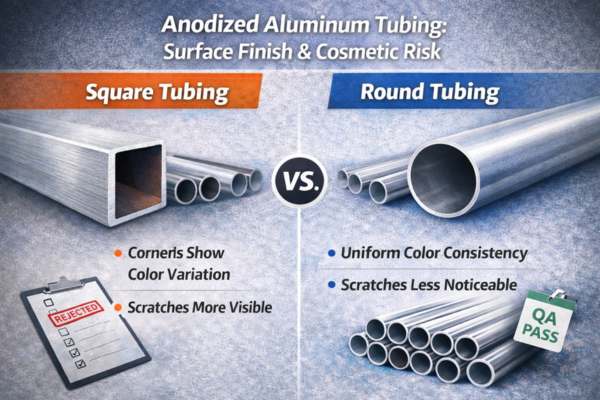
For retail-facing products, appearance matters as much as structure.
Round tubing shows:
- More uniform anodizing thickness
- Fewer visible color variations
- Less noticeable scratches
Square tubing:
- Corners may anodize differently
- Flat faces reveal defects more easily
- Requires stricter cosmetic inspection
This is a key reason round tubing is often preferred for products sold through large retail programs.
Assembly, Grip, and User Experience
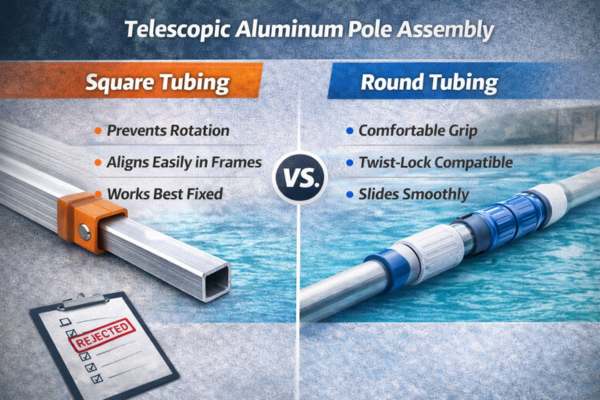
How a product feels in use often decides repeat orders.
Square tubing advantages:
- Prevents rotation in fixed assemblies
- Aligns easily with brackets and frames
- Works well in structural designs
Round tubing advantages:
- More comfortable to grip
- Works smoothly with twist-lock systems
- Slides better in telescopic designs
This is why most telescopic pool poles and extension poles use round tubing, even when square tubing appears stronger on paper.
Cost Reality: Why Price per Meter Is Misleading

Many buyers compare tubing only by material price. That often leads to wrong decisions.
Real cost drivers include:
- Extrusion speed and scrap rate
- Straightening and cutting yield
- Finishing rejection rate
- Assembly efficiency
In many projects, round tubing ends up cheaper per finished unit, not because the aluminum is cheaper, but because fewer parts fail later.
Typical Applications: Choosing the Right Shape

Round tubing is commonly used for:
- Pool cleaning poles
- Telescopic extension poles
- Handheld consumer products
- Products requiring smooth rotation
Square tubing is commonly used for:
- Frames and racks
- Fixed structural supports
- Industrial housings
- Assemblies requiring anti-rotation
Matching shape to application avoids unnecessary cost and redesign.
Buyer Checklist: How to Decide Before Sampling
Before locking your design, ask:
- Will the product be handheld or fixed?
- Does it need to rotate or telescope?
- How strict are cosmetic standards?
- Is weight a selling point or a concern?
- Will it be sold through retail or industrial channels?
Clear answers here reduce redesign risk later.
FAQ: Square Tubing vs Round Tubing
Is square tubing always stronger than round tubing?
No. Strength depends on load direction, wall thickness, and length.
Which shape reduces cosmetic rejection risk?
Round tubing typically shows a more consistent surface finish.
Which shape is easier to source globally?
Round tubing is more standardized and easier to scale.
Which is better for outdoor use?
Both perform well when properly anodized; coating quality matters more than shape.
Talk to a Manufacturer Before You Finalize
Choosing tubing shape early affects cost, quality, and delivery.
With aluminum extrusion experience dating back to 2002, Xingyong supports OEM and retail buyers with:
- 14 extrusion lines up to 2000T
- In-house anodizing and deep processing
- Monthly output of 3,000 tons
You can request samples, review drawings, or discuss your application before committing to production.
👉 Contact our export team to move forward with confidence.






